How to check WWN and Multipathing on Windows Server
Introduction
World Wide Name (WWN) and multipathing are crucial elements in storage management for Windows Servers. This guide will walk you through the process of checking WWN and multipathing across different Windows Server versions.
Windows Server 2012-2022
Checking World Wide Names (WWNs) and iSCSI IQNs
Use the following PowerShell command:
Get-InitiatorPortChecking ISCSI Connections
Execute this PowerShell command:
Get-IscsiTargetChecking MPIO Connections
For MPIO (Multipath I/O) connections to SAN, use:
mpclaim -s -dChecking Multipath for Specific Disks
List all disks:
list diskCheck multipath for a specific disk (e.g., Disk 0):
mpclaim -s -d 0Suggested Read: Top 50 PowerShell Commands for Daily Use
Windows Server 2008
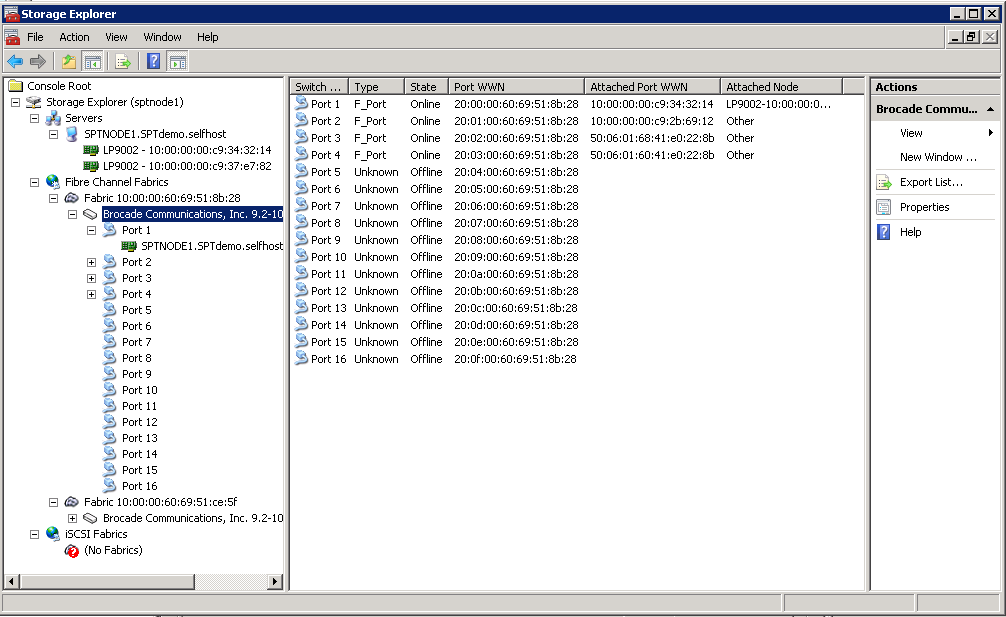
Use the Storage Explorer tool to view:
- FC switches in your storage fabric
- Details about switch port connections
- Information about other servers connected to the storage fabric
- HBA and LUN information
Windows Server 2003/2000
Using FCINFO (Fibre Channel Information Tool)
Run the “fcinfo” command in Command Prompt. It will show up HBA connected to the server with WWN
- Download FCINFO from Microsoft Download Center
- Run the following command in the Command Prompt:
fcinfoThis will display HBA information, including WWN.
Model-Based Utilities
Some vendor-specific utilities include:
- HBAnyware utility
- SANsurfer utility
- Hitachi Storage Commands:
dlnkmgr view -path # Check multipath output
dlnkmgr view -drv # Check current settings
dlnkmgr set -lb on -lbtype rr # Set load balancing
dlnkmgr set -pchk on -intvl 10 # Set path Health Checking
dlknmgr set -afb on # Set Automatic FailbackConclusion
Understanding how to check WWN and multipathing is essential for efficient storage management in Windows Server environments. By following this guide, you can effectively manage these aspects across various Windows Server versions and utilize vendor-specific tools when necessary.
Also Check: Unable to join machines to the domain. Error Message “The Specified User already exists”
- Why should you automate Active Directory cleanup? - 17 June 2025
- Troubleshooting: Unable to Add Instance Failover Group to Azure SQL Managed Instance - 4 March 2025
- 10 Azure Virtual Desktop (AVD) Cost-Optimization Strategies for 2025 💡💰 - 22 February 2025